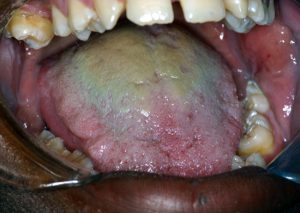
Hairy tongue is a commonly found clinical lesion.
So, do you know the cause of it? Although the cause is unknown, it is most frequently seen in patients that do not brush their tongue. It occurs when a patient doesn’t naturally exfoliate the epithelial cells on the dorsal surface of the tongue. The result is an elongation of the filiform papillae.
Hairy tongue can also be seen in the following cases (predisposing factors):
- taking broad spectrum antibiotics
- taking systemic steroids
- heavy smokers– undergoing radiation therapy
- in those with candida albicans
- suffering from febrile illnesses
- in those with xerostomia
One of the “cooler” things that can be seen with hairy tongue is the possibility of different colors.
The colors will vary somewhat with the cause of why it’s present and what the patient is doing. A white color is typically indicative of elongation of the filiform papillae, whereas black hairy tongue is the result of chromogenic (Aspergillus) bacteria. Other external factors will change the color as well. If the patient is a smoker, you will see a brown to black coloration. Some foods can cause a color change and depending on what the food is, different color such as green, red, etc…. can be seen.

